Stock Split definition:
Stock split is a corporate action that increases the number of shares for a company but without any changes in stock’s market capitalization.
Imagine you own 10 000 shares of company X and each share worth 20$.After a 2 for 1 split, you will own 20 000 shares and each one worth 10$.
As market capitalization remains the same, there isn’t any change in the true value of the company.
There are many stock split ratios; the most common are 2 for 1, 3 for 2 and 3 for 1.
When do stock split?
Companies can decide to implement a stock split for many reasons.
One common reason is that when their stock price gets too high, it will scare off some small investors, also it will increase liquidity and reduce bid/ask spread.
Back-test problems:
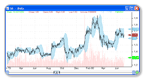
When doing a back-test in some technical analysis software, you probably come up with some problems regarding stock split.
Lot of these software don’t incorporate stock split in their data and this will result in some error in the back-testing.
As an example:
Imagine a trading system back-test that picks Stock X.It buy X at 20$ and then sell it at 9$. (Loss of more than -50%)
In reality, there is a great chance that when the system picked the stock X, the company made a 2 for 1 split and that’s why the stock dropped from 20$ to 9$.
So in fact, the real result will be a performance of -10% (Buy at 10$ and sell at 9$).
The opposite can happen, when you see big gaps in stock chart, it is probably due to reverse stock split.
A 1 for 2 stock splits means that for every two shares you own, you get one share. It’s the opposite of 2-for1 stock split.
skip to main |
skip to sidebar
Provide you with : - Stock picks that performed very well since 5 years. - Interesting backtest results. - Tutorials (including fundamental analysis,technical analysis,option hedging...)